有很多文章都介绍了在应用层面怎么调用 CLONE 的参数来进行 namespace 隔离,于是好奇 namespace 在 kernel 层面是怎么实现的,比如 kernel 需要做哪些改动来提供 namespace 的功能。
应用层面进行namespace隔离的方法
对于应用程序,例如 docker, 可以通过调用 clone(), unshare(), setns() 来对 namespace 进行操作。Coolshell 有几篇通俗易懂的文章可供详细了解[1].
例如,使用系统封装好的 unshare 命令,可以在另一个 mount namespace 运行一个 shell.
[root@ip-172-31-16-186 tmp]# echo $$
32421
在这个 shell 中挂着一个文件系统。
[root@ip-172-31-16-186 tmp]# cat /proc/mounts
/dev/loop0 /mnt ext4 rw,relatime,data=ordered 0 0
从其他shell中,是看不到这个挂载点的。
--> No loop device.
从 /proc/(pid)/ns 中,可以看到这个 unshare 了的 shell 跟普通 shell 的 mnt namespace 是不一样的。
total 0
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 Dec 6 03:29 cgroup -> cgroup:[4026531835]
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 Dec 6 03:29 ipc -> ipc:[4026531839]
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 Dec 6 03:29 mnt -> mnt:[4026531840] ##<----
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 Dec 6 03:29 net -> net:[4026532041]
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 Dec 6 03:29 pid -> pid:[4026531836]
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 Dec 6 03:29 pid_for_children -> pid:[4026531836]
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 Dec 6 03:29 user -> user:[4026531837]
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 Dec 6 03:29 uts -> uts:[4026531838]
[root@ip-172-31-16-186 ~]# ls -l /proc/32421/ns/
total 0
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 Dec 6 03:29 cgroup -> cgroup:[4026531835]
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 Dec 6 03:29 ipc -> ipc:[4026531839]
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 Dec 6 03:29 mnt -> mnt:[4026532210] ##<----
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 Dec 6 03:29 net -> net:[4026532041]
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 Dec 6 03:29 pid -> pid:[4026531836]
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 Dec 6 03:29 pid_for_children -> pid:[4026531836]
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 Dec 6 03:29 user -> user:[4026531837]
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 Dec 6 03:29 uts -> uts:[4026531838]
如果对 unshare -m 这个命令进行 strace, 可以看到它其实调用了 unshare() 的系统调用,并且带上了 CLONE_NEWNS 的 flag.
465 05:10:37.376822 unshare(CLONE_NEWNS) = 0
465 05:10:37.376898 mount("none", "/", NULL, MS_REC|MS_PRIVATE, NULL) = 0 //<--- MS_REC|MS_PRIVATE will make the mount point private, so the mount/umount operation would not propagate. See mount(2).
465 05:10:37.376931 execve("/bin/bash", ["-bash"], ......) = 0
我们也可以自己写个程序,通过 clone() 的 CLONE_NEWNS 来实现 mount namespace 的隔离。
* Source: https://coolshell.cn/articles/17010.html
* Modified slightly by feichashao.com
***/
#define _GNU_SOURCE
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <sys/mount.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sched.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <unistd.h>
/* 定义一个给 clone 用的栈,栈大小1M */
#define STACK_SIZE (1024 * 1024)
static char container_stack[STACK_SIZE];
char* const container_args[] = {
"/bin/bash",
NULL
};
int container_main(void* arg)
{
printf("Container - inside the container!\n");
/* 直接执行一个shell,以便我们观察这个进程空间里的资源是否被隔离了 */
mount("none", "/", NULL, MS_REC|MS_PRIVATE, NULL); // make mount point private.
execv(container_args[0], container_args);
printf("Something's wrong!\n");
return 1;
}
int main()
{
printf("Parent - start a container!\n");
/* 调用clone函数,其中传出一个函数,还有一个栈空间的(为什么传尾指针,因为栈是反着的) */
int container_pid = clone(container_main, container_stack+STACK_SIZE, CLONE_NEWNS | SIGCHLD, NULL);
/* 等待子进程结束 */
waitpid(container_pid, NULL, 0);
printf("Parent - container stopped!\n");
return 0;
}
编译运行这个程序,可以看到,由这个程序clone出来的子进程已经运行在一个新的 mnt namespace 中。
[root@ip-172-31-16-186 tmp]# ./mnt_namespace
Parent - start a container!
Container - inside the container!
[root@ip-172-31-16-186 tmp]# ls -l /proc/self/ns/ | grep mnt
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 Dec 6 05:54 mnt -> mnt:[4026532210]
[root@ip-172-31-16-186 tmp]# ls -l /proc/1/ns/ | grep mnt
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 Dec 6 03:29 mnt -> mnt:[4026531840]
尝试在这个新的 mnt namespace 中挂在一个文件系统。
[root@ip-172-31-16-186 tmp]# cat /proc/mounts | grep mnt
/dev/loop0 /mnt ext4 rw,relatime,data=ordered 0 0
(在另一个shell中,看不到同样的挂载点)
[root@ip-172-31-16-186 ~]# cat /proc/mounts | grep mnt
--> null
Kernel-2.4.19中 mount namespace 的实现
Kernel 的第一个 namespace 功能是在 2.4.19 这个版本提供的,当时只有 mount namespace, 于是 CLONE_NEWNS 这个通用的名字后面就变成 mount namespace 专属了。为了方便学习 namespace 在kernel的实现,我们可以从 2.4.19 内核的代码开始。
在 linux-2.4.18 -> linux-2.4.19 的 patch 中,可以看到一些变动。
(1) 在 sched.h 中加入了 CLONE_NEWNS 的定义。在 task_struct 里加入了 namespace 的元素。
--- linux-2.4.18/include/linux/sched.h Fri Dec 21 09:42:03 2001
+++ linux-2.4.19/include/linux/sched.h Fri Aug 2 17:39:45 2002
+#define CLONE_NEWNS 0x00020000 /* New namespace group? */
+struct namespace;
(2) 新增了 namespace.h 文件,里面定义了 struct namespace, 以及 put_namespace, exit_namespace, copy_namespace, get_namespace 等函数。
--- linux-2.4.18/include/linux/namespace.h Wed Dec 31 16:00:00 1969
+++ linux-2.4.19/include/linux/namespace.h Fri Aug 2 17:39:45 2002
struct namespace {
atomic_t count;
struct vfsmount * root;
struct list_head list;
struct rw_semaphore sem;
};
static inline void put_namespace(struct namespace *namespace)
{
if (atomic_dec_and_test(&namespace->count)) {
down_write(&namespace->sem);
spin_lock(&dcache_lock);
umount_tree(namespace->root);
spin_unlock(&dcache_lock);
up_write(&namespace->sem);
kfree(namespace);
}
}
static inline void exit_namespace(struct task_struct *p)
{
struct namespace *namespace = p->namespace;
if (namespace) {
task_lock(p);
p->namespace = NULL;
task_unlock(p);
put_namespace(namespace);
}
}
extern int copy_namespace(int, struct task_struct *);
static inline void get_namespace(struct namespace *namespace)
{
atomic_inc(&namespace->count);
}
(3) 在 fork 中,添加了 CLONE_NEWNS 的 routine.
--- linux-2.4.18/kernel/fork.c Mon Feb 25 11:38:13 2002
+++ linux-2.4.19/kernel/fork.c Fri Aug 2 17:39:46 2002
@@ -19,7 +19,9 @@
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/vmalloc.h>
#include <linux/completion.h>
+#include <linux/namespace.h>
#include <linux/personality.h>
+#include <linux/compiler.h>
@@ -569,6 +581,9 @@
struct task_struct *p;
struct completion vfork;
+ if ((clone_flags & (CLONE_NEWNS|CLONE_FS)) == (CLONE_NEWNS|CLONE_FS))
+ return -EINVAL;
+
@@ -671,9 +688,11 @@
goto bad_fork_cleanup_fs;
if (copy_mm(clone_flags, p))
goto bad_fork_cleanup_sighand;
+ if (copy_namespace(clone_flags, p))
+ goto bad_fork_cleanup_mm;
retval = copy_thread(0, clone_flags, stack_start, stack_size, p, regs);
if (retval)
- goto bad_fork_cleanup_mm;
+ goto bad_fork_cleanup_namespace;
p->semundo = NULL;
@@ -740,6 +759,8 @@
fork_out:
return retval;
+bad_fork_cleanup_namespace:
+ exit_namespace(p);
bad_fork_cleanup_mm:
exit_mm(p);
bad_fork_cleanup_sighand:
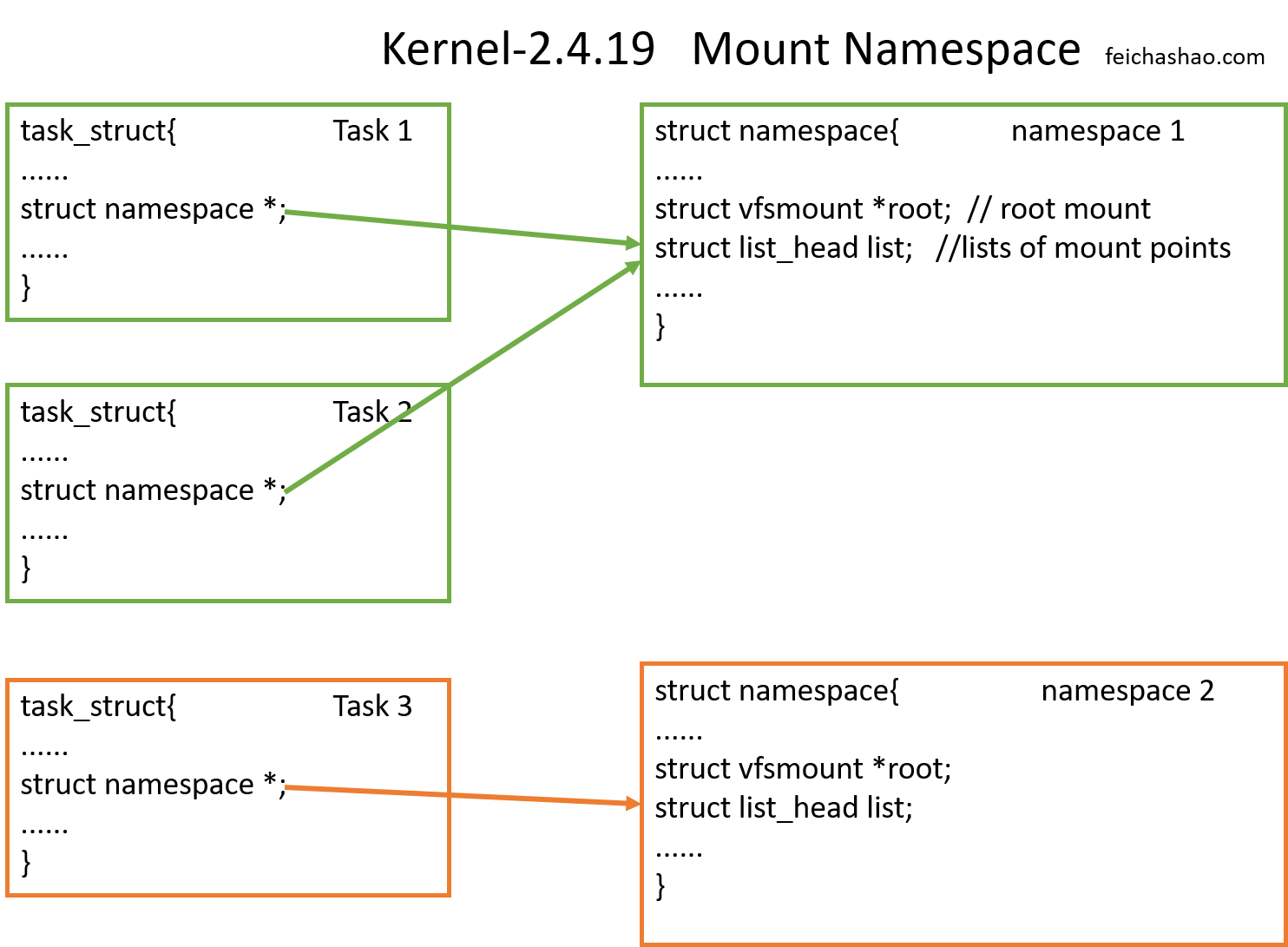
可以看到,Kernel-2.4.19中,namespace 的数据结构是如下图这样的。每个进程的 task_struct 会记录一个 namespace 指针,指向对应的 namespace. 如果与其他进程共用相同的 namespace,则指向相同的 namespace.
在 Kernel-2.4.19 中,调用一个带 CLONE_NEWNS 参数的 fork() 是按如下步骤实现的。
(0) 在操作系统启动的开始,要给第一个程序初始化一个 namespace 的 struct. 需要留意的是,namespace->list 里连接的不是 namespace, 而是 vfsmount.
static void __init init_mount_tree(void)
{
struct vfsmount *mnt;
struct namespace *namespace;
struct task_struct *p;
mnt = do_kern_mount("rootfs", 0, "rootfs", NULL);
if (IS_ERR(mnt))
panic("Can't create rootfs");
namespace = kmalloc(sizeof(*namespace), GFP_KERNEL); // 分配 namespace 空间
if (!namespace)
panic("Can't allocate initial namespace");
atomic_set(&namespace->count, 1); // 初始化
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&namespace->list); //
init_rwsem(&namespace->sem); //
list_add(&mnt->mnt_list, &namespace->list); //<--- the first added list entry is struct vfsmount
namespace->root = mnt; //
init_task.namespace = namespace;
read_lock(&tasklist_lock);
for_each_task(p) {
get_namespace(namespace);
p->namespace = namespace;
}
read_unlock(&tasklist_lock);
set_fs_pwd(current->fs, namespace->root, namespace->root->mnt_root);
set_fs_root(current->fs, namespace->root, namespace->root->mnt_root);
}
(1) 程序进行系统调用,进入到内核的 do_fork().
int do_fork(unsigned long clone_flags, unsigned long stack_start,
struct pt_regs *regs, unsigned long stack_size)
{
int retval;
struct task_struct *p;
struct completion vfork;
if ((clone_flags & (CLONE_NEWNS|CLONE_FS)) == (CLONE_NEWNS|CLONE_FS))
return -EINVAL;
....
if (copy_namespace(clone_flags, p)) // 调用 copy_namespace 来创建新的 namespace.
goto bad_fork_cleanup_mm;
....
bad_fork_cleanup_namespace:
exit_namespace(p);
......
}
(2) 在 copy_namespace() 中,会判断 fork 的时候有没有 CLONE_NEWNS 的 flag, 有的话复制一个新的namespace到fork出来的进程中。
int copy_namespace(int flags, struct task_struct *tsk)
{
struct namespace *namespace = tsk->namespace;
struct namespace *new_ns;
struct vfsmount *rootmnt = NULL, *pwdmnt = NULL, *altrootmnt = NULL;
struct fs_struct *fs = tsk->fs;
if (!namespace)
return 0;
get_namespace(namespace); //将源 namespace 的计数器加一,防止该namespace被释放。
if (! (flags & CLONE_NEWNS))
return 0;
if (!capable(CAP_SYS_ADMIN)) { // 进行这项操作的程序需要有 CAP_SYS_ADMIN 的 capability.
put_namespace(namespace);
return -EPERM;
}
new_ns = kmalloc(sizeof(struct namespace *), GFP_KERNEL); // 创建一个 namespace 数据结构
if (!new_ns)
goto out;
atomic_set(&new_ns->count, 1); // 初始化这个 namespace, 设置 count=1
init_rwsem(&new_ns->sem); // 初始化信号量锁
new_ns->root = NULL;
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&new_ns->list); // 初始化链表
down_write(&tsk->namespace->sem);
/* First pass: copy the tree topology */
new_ns->root = copy_tree(namespace->root, namespace->root->mnt_root); //复制挂载树?
spin_lock(&dcache_lock);
list_add_tail(&new_ns->list, &new_ns->root->mnt_list); //
spin_unlock(&dcache_lock);
/* Second pass: switch the tsk->fs->* elements */
if (fs) {
struct vfsmount *p, *q;
write_lock(&fs->lock);
// 深度复制挂载树,把原namespace的挂载内容复制到新的namespace中?
p = namespace->root;
q = new_ns->root;
while (p) {
if (p == fs->rootmnt) {
rootmnt = p;
fs->rootmnt = mntget(q);
}
if (p == fs->pwdmnt) {
pwdmnt = p;
fs->pwdmnt = mntget(q);
}
if (p == fs->altrootmnt) {
altrootmnt = p;
fs->altrootmnt = mntget(q);
}
p = next_mnt(p, namespace->root);
q = next_mnt(q, new_ns->root);
}
write_unlock(&fs->lock);
}
up_write(&tsk->namespace->sem);
tsk->namespace = new_ns; // tsk 是 fork 出来的 task, 将它的 namespace 指向复制完成的 new_ns.
if (rootmnt)
mntput(rootmnt);
if (pwdmnt)
mntput(pwdmnt);
if (altrootmnt)
mntput(altrootmnt);
put_namespace(namespace); //把源 namespace 计数器复原
return 0;
out:
put_namespace(namespace);
return -ENOMEM;
}
这样,在 fork 出来的程序里,就有了一个新的 namespace. 函数调用总结如图。

在 Kernel-2.4.19 中,内核执行一个 mount() 操作,也会考虑到 namespace.
(1) 程序进行系统调用,内核执行 sys_mount(). 它会调用 do_mount() 做实际的工作。
asmlinkage long sys_mount(char * dev_name, char * dir_name, char * type,
unsigned long flags, void * data)
{
int retval;
unsigned long data_page;
unsigned long type_page;
unsigned long dev_page;
char *dir_page;
// 省略
lock_kernel();
retval = do_mount((char*)dev_page, dir_page, (char*)type_page,
flags, (void*)data_page); //<-------
unlock_kernel();
// 省略
}
(2) 随后会 do_mount() 调用 do_add_mount().
unsigned long flags, void *data_page)
{
struct nameidata nd;
int retval = 0;
int mnt_flags = 0;
// 省略
if (flags & MS_REMOUNT)
retval = do_remount(&nd, flags & ~MS_REMOUNT, mnt_flags,
data_page);
else if (flags & MS_BIND)
retval = do_loopback(&nd, dev_name, flags & MS_REC);
else if (flags & MS_MOVE)
retval = do_move_mount(&nd, dev_name);
else
retval = do_add_mount(&nd, type_page, flags, mnt_flags,
dev_name, data_page); //<<---------
path_release(&nd);
return retval;
}
(3) 在 do_add_mount() 中,do_kernel_mount() 会进行文件系统相关的操作,返回一个 vfsmount 结构,记录挂载点相关的信息。
graft_tree() 会把得到的 vfsmount 加入到 namespace 的 list 之中去,这个 namespace 会多一个挂载点。// TODO:此话未经验证
int mnt_flags, char *name, void *data)
{
struct vfsmount *mnt;
int err;
if (!type || !memchr(type, 0, PAGE_SIZE))
return -EINVAL;
/* we need capabilities... */
if (!capable(CAP_SYS_ADMIN))
return -EPERM;
mnt = do_kern_mount(type, flags, name, data); // 做 mount 的动作,获得一个 vfsmount 结构。
err = PTR_ERR(mnt);
if (IS_ERR(mnt))
goto out;
down_write(¤t->namespace->sem);
/* Something was mounted here while we slept */
while(d_mountpoint(nd->dentry) && follow_down(&nd->mnt, &nd->dentry))
;
err = -EINVAL;
if (!check_mnt(nd->mnt))
goto unlock;
/* Refuse the same filesystem on the same mount point */
err = -EBUSY;
if (nd->mnt->mnt_sb == mnt->mnt_sb && nd->mnt->mnt_root == nd->dentry)
goto unlock;
mnt->mnt_flags = mnt_flags;
err = graft_tree(mnt, nd); // 将这个 vfsmount 结构添加到 namespace 的 list 里。这个 vfsmount 结构就是一个挂载点?
unlock:
up_write(¤t->namespace->sem);
mntput(mnt);
out:
return err;
}
在现代 kernel (4.14) 的实现
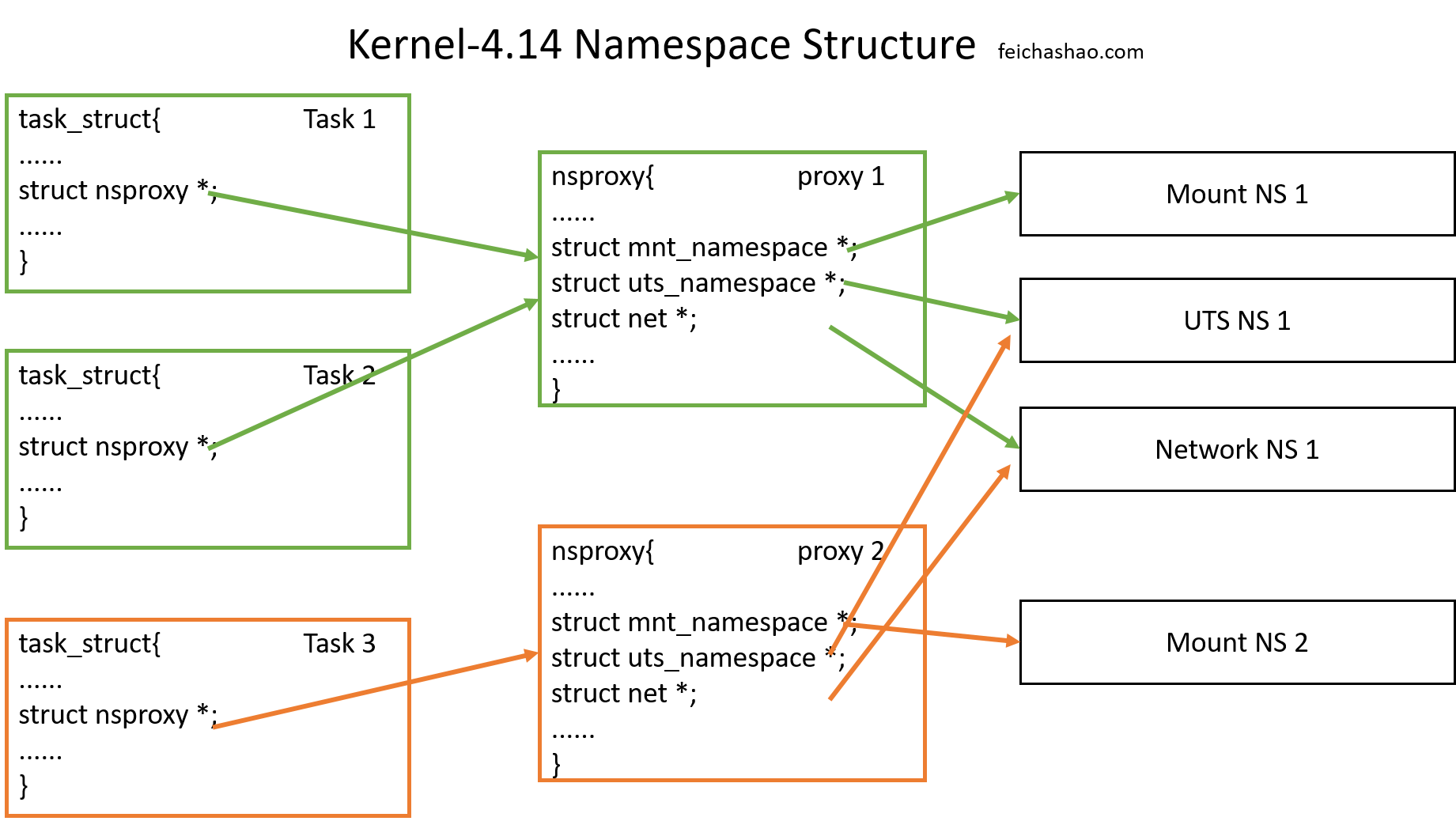
在有了 mount namespace 之后,陆陆续续有了其他 namespace。于是,在现代的kernel,有一个 nsproxy 结构来存放不同 namespace 的指针。
在 task_struct 中,存放着一个指向 struct nsproxy 的 *nsproxy.
struct task_struct {
// 省略
/* Namespaces: */
struct nsproxy *nsproxy;
// 省略
}
nsproxy.h 定义了 struct nsproxy.
/*
* A structure to contain pointers to all per-process
* namespaces - fs (mount), uts, network, sysvipc, etc.
*
* The pid namespace is an exception -- it's accessed using
* task_active_pid_ns. The pid namespace here is the
* namespace that children will use.
*
* 'count' is the number of tasks holding a reference.
* The count for each namespace, then, will be the number
* of nsproxies pointing to it, not the number of tasks.
*
* The nsproxy is shared by tasks which share all namespaces.
* As soon as a single namespace is cloned or unshared, the
* nsproxy is copied.
*/
struct nsproxy {
atomic_t count;
struct uts_namespace *uts_ns;
struct ipc_namespace *ipc_ns;
struct mnt_namespace *mnt_ns;
struct pid_namespace *pid_ns_for_children;
struct net *net_ns;
struct cgroup_namespace *cgroup_ns;
};
数据结构如图。如果新建的程序使用与父进程相同的所有 namespace,则直接指向原来的 nsproxy. 如果其中一个 namespace 与父进程不同,则会新建一个 nsproxy,把不一样的 namespace 指向相应的地方。
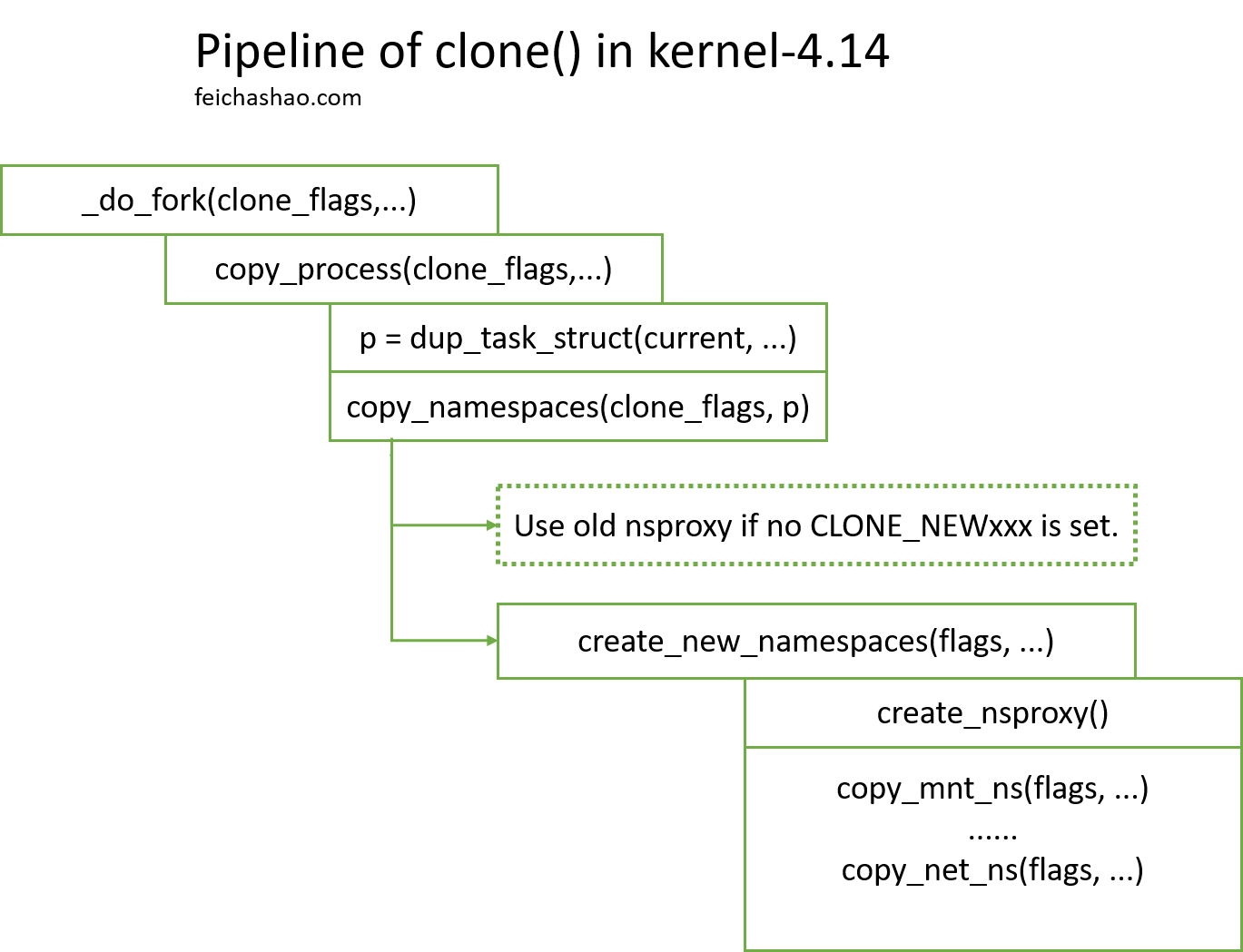
当要 clone() 一个进程的时候,如果 clone() 带上了 CLONE_NEWNS(mount), CLONE_NEWUTS(UTS, 隔离hostname之类), CLONE_NEWIPC(ipc), CLONE_NEWPID(pid), CLONE_NEWNET(network), CLONE_NEWCGROUP(cgroup)等 flag, kernel会为 clone 出来的进程创建一个新的 nsproxy, 指向相应的新的 namespace. 假设我传入了 CLONE_NEWNS 的 flag, clone() 是这样操作的:
(1) 从系统调用进入 _do_fork(), 随后进入 copy_process(), 它的其中有一步是 copy_namespace().
SYSCALL_DEFINE5(clone, unsigned long, clone_flags, unsigned long, newsp,
int __user *, parent_tidptr,
int __user *, child_tidptr,
unsigned long, tls)
{
return _do_fork(clone_flags, newsp, 0, parent_tidptr, child_tidptr, tls);
}
/*
* Ok, this is the main fork-routine.
*
* It copies the process, and if successful kick-starts
* it and waits for it to finish using the VM if required.
*/
long _do_fork(unsigned long clone_flags,
unsigned long stack_start,
unsigned long stack_size,
int __user *parent_tidptr,
int __user *child_tidptr,
unsigned long tls)
{
// 省略
p = copy_process(clone_flags, stack_start, stack_size,
child_tidptr, NULL, trace, tls, NUMA_NO_NODE);
// 省略
}
/*
* This creates a new process as a copy of the old one,
* but does not actually start it yet.
*
* It copies the registers, and all the appropriate
* parts of the process environment (as per the clone
* flags). The actual kick-off is left to the caller.
*/
static __latent_entropy struct task_struct *copy_process(
unsigned long clone_flags,
unsigned long stack_start,
unsigned long stack_size,
int __user *child_tidptr,
struct pid *pid,
int trace,
unsigned long tls,
int node)
{
int retval;
struct task_struct *p;
struct multiprocess_signals delayed;
// 省略
p = dup_task_struct(current, node); //把父进程的task_struct复制到新的进程中。
// 省略
retval = copy_namespaces(clone_flags, p); //创建新的 namespace.
// 省略
}
(2) copy_namespace() 首先会判断是否需要创建新的 namespace,如果不需要,则直接返回,让新进程的 nsproxy 指向跟父进程一样的 nsproxy. 这里假设传入了CLONE_NEWNS,所以会执行 create_new_namespaces() 来创建新的 namespace.
/*
* called from clone. This now handles copy for nsproxy and all
* namespaces therein.
*/
int copy_namespaces(unsigned long flags, struct task_struct *tsk)
{
struct nsproxy *old_ns = tsk->nsproxy;
struct user_namespace *user_ns = task_cred_xxx(tsk, user_ns);
struct nsproxy *new_ns;
if (likely(!(flags & (CLONE_NEWNS | CLONE_NEWUTS | CLONE_NEWIPC |
CLONE_NEWPID | CLONE_NEWNET |
CLONE_NEWCGROUP)))) { //没有传入Namespace的flag, 不需要创建新的nsproxy.
get_nsproxy(old_ns); // 原nsproxy计数器加1
return 0;
}
if (!ns_capable(user_ns, CAP_SYS_ADMIN))
return -EPERM;
// 省略
new_ns = create_new_namespaces(flags, tsk, user_ns, tsk->fs); //创建新的 nsproxy,并创建相应的 namespace.
if (IS_ERR(new_ns))
return PTR_ERR(new_ns);
tsk->nsproxy = new_ns;
return 0;
}
(3) 在 create_new_namespaces() 中,会创建一个新的 nsproxy. 后面会调用 copy_xxx() 等函数,分别创建新的 namespaces。例如,如果带有 CLONE_NEWNS 的 flag, copy_mnt_ns() 会创建并返回一个新的 mount namespace, 否则返回原来的 mount namespace.
/*
* Create new nsproxy and all of its the associated namespaces.
* Return the newly created nsproxy. Do not attach this to the task,
* leave it to the caller to do proper locking and attach it to task.
*/
static struct nsproxy *create_new_namespaces(unsigned long flags,
struct task_struct *tsk, struct user_namespace *user_ns,
struct fs_struct *new_fs)
{
struct nsproxy *new_nsp;
int err;
new_nsp = create_nsproxy();
// 省略
new_nsp->mnt_ns = copy_mnt_ns(flags, tsk->nsproxy->mnt_ns, user_ns, new_fs);
// 省略
new_nsp->uts_ns = copy_utsname(flags, user_ns, tsk->nsproxy->uts_ns);
// 省略
new_nsp->ipc_ns = copy_ipcs(flags, user_ns, tsk->nsproxy->ipc_ns);
// 省略
new_nsp->pid_ns_for_children =
copy_pid_ns(flags, user_ns, tsk->nsproxy->pid_ns_for_children);
// 省略
new_nsp->cgroup_ns = copy_cgroup_ns(flags, user_ns,
tsk->nsproxy->cgroup_ns);
// 省略
new_nsp->net_ns = copy_net_ns(flags, user_ns, tsk->nsproxy->net_ns);
// 省略
return new_nsp;
}
(4) copy_mnt_ns() 的 routine 跟 kernel-2.4.19 的 copy_namespace() 就很像了,先复制挂载树的拓扑,再深度复制每一个挂载点。
__latent_entropy
struct mnt_namespace *copy_mnt_ns(unsigned long flags, struct mnt_namespace *ns,
struct user_namespace *user_ns, struct fs_struct *new_fs)
{
struct mnt_namespace *new_ns;
struct vfsmount *rootmnt = NULL, *pwdmnt = NULL;
struct mount *p, *q;
struct mount *old;
struct mount *new;
int copy_flags;
// 省略
old = ns->root;
new_ns = alloc_mnt_ns(user_ns);
// 省略
/* First pass: copy the tree topology */
new = copy_tree(old, old->mnt.mnt_root, copy_flags);
// 省略
new_ns->root = new;
list_add_tail(&new_ns->list, &new->mnt_list);
/*
* Second pass: switch the tsk->fs->* elements and mark new vfsmounts
* as belonging to new namespace. We have already acquired a private
* fs_struct, so tsk->fs->lock is not needed.
*/
p = old;
q = new;
while (p) {
q->mnt_ns = new_ns;
new_ns->mounts++;
if (new_fs) {
if (&p->mnt == new_fs->root.mnt) {
new_fs->root.mnt = mntget(&q->mnt);
rootmnt = &p->mnt;
}
if (&p->mnt == new_fs->pwd.mnt) {
new_fs->pwd.mnt = mntget(&q->mnt);
pwdmnt = &p->mnt;
}
}
p = next_mnt(p, old);
q = next_mnt(q, new);
if (!q)
break;
while (p->mnt.mnt_root != q->mnt.mnt_root)
p = next_mnt(p, old);
}
namespace_unlock();
if (rootmnt)
mntput(rootmnt);
if (pwdmnt)
mntput(pwdmnt);
return new_ns;
}
参考文档
[1] Docker基础技术:Linux Namespace(上)
https://coolshell.cn/articles/17010.html
[2] Linux kernel Namespace源码分析
https://blog.csdn.net/WaltonWang/article/details/53900248
[3] Linux Namespace分析——mnt namespace的实现与应用
http://hustcat.github.io/namespace-implement-1/
[4] Deep dive into Linux network namespace
http://hustcat.github.io/deep-dive-into-net-namespace/